A holder in due course can freely sell or assign notes receivable to others. Notes receivable stem from formally lending sums of money to other entities. The borrower signs this legal agreement promising repayment of the principal amount plus any interest. If the debtor defaults, the note serves as evidence to compel payment. Interest from note receivable will be recorded as interest income in the income statement. Gear Inc offers specialized Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable outsourcing solutions for businesses aiming to streamline these processes.
Frequently Asked Questions About The Differences Between Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable
This receivable expansion allows a company to attract a more diverse clientele and increase asset potential to further grow the business. Note that in this calculation we expressed the time period as a fraction of a 360-day year because the interest rate is an annual rate and the note life was days. Frequency of a year is the amount of time for the note and can be either days or months. We need the frequency of a year because the interest rate is an annual rate and we may not want interest for an entire year but just for the time period of the note. When notes receivable have terms of less than one year, accounting for short-term notes is relatively straight forward as discussed below. This balance represents 89 days [30 days in January, 28 days in February, 31 days in March] of the the 90 day note.
Trial Balance
When a customer does not pay an account receivable that is due, the company may insist that the customer gives a note in place of the account receivable. This action allows the customer more time to pay the balance due, and the company earns interest on the balance until paid. Also, the company may be able to sell the note to a bank or other financial institution.
- In this case the note receivable is issued to replace an amount due from a customer currently shown as accounts receivable.
- Another opportunity for a company to issue a notes receivable iswhen one business tries to acquire another.
- Therefore, the discount or premium shall be reported in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from or addition to the face amount of the note.
- In some instances, an Accounts Receivable amount may be changed to a Note Receivable by agreement between the company and the customer.
- The date on which the security agreement is initially established is the issue date.
Accounts Receivable Turnover (in Times)
This results in a reduction in the principal amount owing upon which the interest is calculated. Dino-Kleen, a customer of Terrance Inc. owes a $10,000 invoice that is past due. Terrance Inc. agrees to grant Dino-Kleen a longer period of time to pay the invoice in exchange for 5% interest. This means the interest on the note is earned in the January, February, March, and April accounting periods.
Time Value of Money
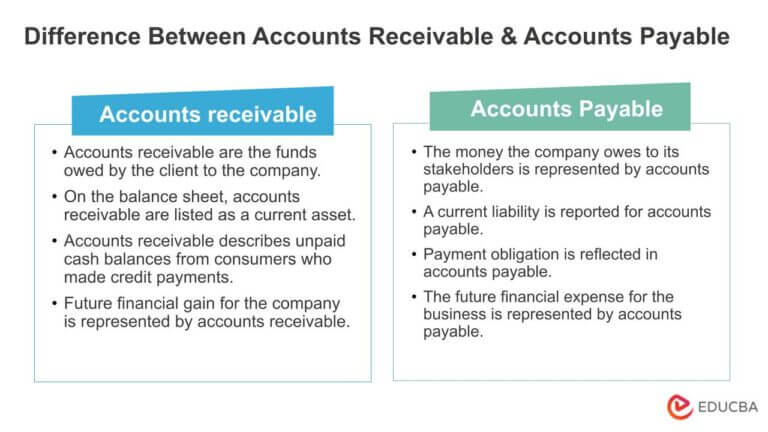
Determining present values requires an analysis of cash flows using interest rates and time lines, as illustrated next. In many ways, accounts payable is the opposite of accounts receivable. Accounts payable is a current liability on the balance sheet, while accounts receivable is a current asset.
Legal Standing
Our services ensure accuracy, efficiency, and financial control, freeing companies to concentrate on growth and core operations. Entities that anticipate prepayments in applying the interest method shall disclose that policy and the significant assumptions underlying the prepayment estimates. (a)”One year after date, I promise to pay…” When the maturity is expressed in years, the note matures on the same day of the same month as the date of the note in the year of maturity. Below are some examples with journal entries involving various stated rates compared to market rates. Cash amount equals the $10,000 face value of the amount of the note receivable plus the full amount of the interest being paid.
Periodic interest accrued is recorded in Interest Revenue and Interest Receivable. The following example uses months but the calculation could also be based on a 365-day year. Just as was the case with accounts receivable, there is a possibility that the holder of the note receivable will not be able to collect some or all of the amounts owing. When the investment in a note receivable becomes impaired for any reason, the receivable is re-measured at the present value of the currently expected cash flows at the loan’s original effective interest rate. Here the principal amount is the amount burrowed by the payee from the issuer.
Interest Income or Interest Revenue is an Revenue account so it has a normal credit balance. Interest Income or Interest Revenue is increased on the credit (right) side of the account and decreased on specialized tax services sts accounting method: pwc the debit (left) side of the account. The account name used will be specified in the company’s Chart of Accounts. We provide third-party links as a convenience and for informational purposes only.
For example, a company may have an outstanding account receivable in the amount of $1,000. The customer negotiates with the company on June 1 for a six-month note maturity date, 12% annual interest rate, and $250 cash up front. The difference between a short-term note and a long-term note is the length of time to maturity.
A note receivable is an unconditional written promise to pay a specific sum of money on demand or on a defined future date and is supported by a formal written promissory note. For this reason, notes are negotiable instruments the same as cheques and bank drafts. Or, we can combine this entry with the journal entry for the repayment of the note. Rather than using Interest Receivable for the one day of interest in April, we record it as part of the cash payment, skipping the step of first entering it in the receivable. Accounts Receivable is a normal business transaction for between a company and its customer.
The cash flow is discounted to a lesser sum that eliminates the interest component—hence the term discounted cash flow. The future amount can be a single payment at the date of maturity or a series of payments over future time periods or some combination of both. As you’ve learned, accounts receivable is typically a moreinformal arrangement between a company and customer that isresolved within a year and does not include interest payments.